-
LONDON: Indian-Origin Teen In UK Gets “Life-Changing” Cancer Treatment - 20 hours ago
-
SILICON VALLEY: All About Pavan Davuluri, New Head Of Microsoft Windows - 21 hours ago
-
LONDON: UK’s India Gate To Commemorate Role Of Indian Soldiers From World Wars - 2 days ago
-
HARARE: Shri Bramha Kumar appointed as the next Ambassador of India to the Republic of Zimbabwe - April 23, 2024
-
LONDON: Indian-Origin Principal Wins UK Legal Challenge Over School Prayer Ban - April 23, 2024
-
TORONTO: Indian-Origin Doctor Needs ₹ 2 Crore For Legal Fees. Elon Musk Responds - April 22, 2024
-
KINSHASA: India-Democratic Republic of Congo Foreign Office Consultations - April 21, 2024
-
LONDON: UK Court Allows Sale Of Nirav Modi’s Luxury London Apartment - April 21, 2024
-
TEHRAN: Travel advisory for Iran and Israel - April 20, 2024
-
LUXEMBOURG: Shri Saurabh Kumar concurrently accredited as the next Ambassador of India to the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg - April 20, 2024
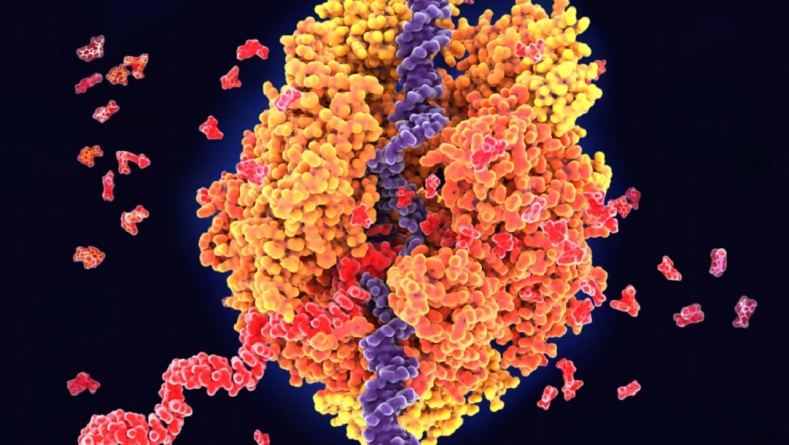
PARIS : 50 years ago, genes eluded electron microscopes
PARIS : Scientists still can’t directly see genes with electron microscopes, but combining the tool with the molecular scissors CRISPR/Cas9 has let researchers visualize genes being transcribed (illustrated) from DNA (blue) into RNA (red).
Molecular biologists can now visualize the larger structures of the cell, such as the nucleus and chromosomes, under the powerful electron microscope. But they have not been able to obtain images of genes (DNA) on the chromosomes. Nor have they been able to see RNA … or the intricate details of cell membranes, enzymes and viruses.
Update
Electron microscopes have become much more powerful over the last 50 years. For instance, in 1981, biophysicist Jacques Dubochet discovered that tiny biological structures supercooled with ethane could be observed in their natural state under an electron microscope. That finding paved the way for cryo-electron microscopy, which scientists use to visualize proteins, viruses and bacteria at the molecular level. Capturing detailed images of genes remains elusive, but scientists are inching closer. In 2021, researchers reported using an electron microscope and the molecular scissors CRISPR/Cas9 to visualize proteins transcribing DNA instructions for two genes into RNA.