-
CANBERRA: India-Australia partnership aims to bridge skill gap for future employment - April 15, 2024
-
HOUSTON: Mumbai boys in the final rounds of FIRST World Robotics competition to be held in Houston - April 14, 2024
-
MADRAS: IIT Madras NPTEL translates thousands of technical courses into several regional languages - April 10, 2024
-
MUMBAI: Shahid Kapoor opens up about the challenges faced by character actors in Bollywood - April 8, 2024
-
NEW DELHI: World Health Day 2024: Date, Theme, History, Significance and Interesting Facts - April 6, 2024
-
LONDON: Indian-Origin Teen In UK Gets “Life-Changing” Cancer Treatment - April 3, 2024
-
BENGALURU: Indian scientists unravel genetic secrets behind lumpy skin disease outbreak - March 30, 2024
-
NEW DELHI: Youngsters’ Increasing Stress Levels, Early Onset of Diseases an Alarming Health Trend: Apollo Hospitals Chief - March 28, 2024
-
MARYLAND: All About Pavan Davuluri, New Head Of Microsoft Windows - March 27, 2024
-
MUMBAI: Pyaar Kiya To Darna Kya turns 26: Kajol says THIS was the symbol of an innocent girl back then - March 27, 2024
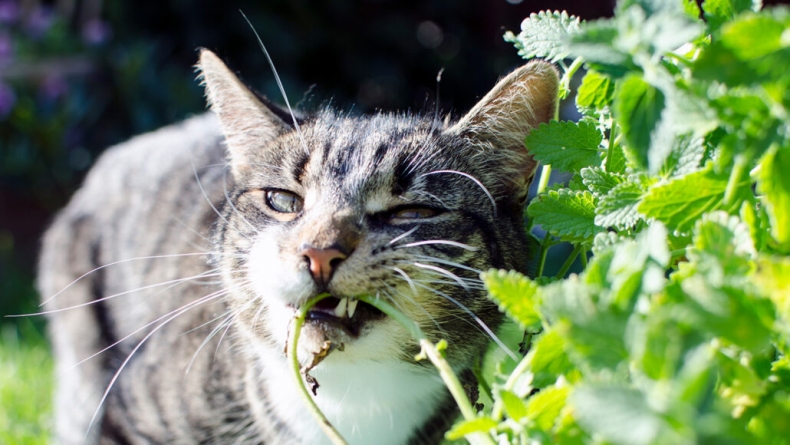
BERLIN: Cats chewing on catnip boosts the plant’s insect-repelling powers
BERLIN: Catnip is known to bug bugs. When a cat chews, licks and destroys catnip, the plant releases more insect-repelling compounds, a new study finds. For many cats, a mere whiff of catnip can send them into a licking, rolling, plant-shredding frenzy.
That destruction amplifies catnip’s natural defenses against insects and its appeal to cats, a new chemical analysis finds. Compared with intact leaves, crushed-up leaves emit more volatile compounds called iridoids, which act as an insect repellant, researchers report June 14 in iScience. The higher emissions also seem to encourage cats to continue rolling around in the remains of the plant, effectively coating themselves in a natural bug spray.
Masao Miyazaki, a biologist at Iwate University in Morioka, Japan, and his colleagues analyzed the chemistry of both catnip (Nepeta cataria) and silver vine (Actinidia polygama), a plant common in Asia that has a similar euphoric effect on cats. Both plants naturally produce iridoids, which discourage insects from snacking on leaves.
As cats toyed with silver vine, the damaged leaves released about 10 times more iridoids than intact leaves did, and also changed the proportion of the chemicals released. The researchers also found that catnip when crushed up released over 20 times more of its insect repellant, mostly a type of iridoid called nepetalactone.
With both plants, lab-made iridoid cocktails mimicking those of damaged catnip and silver vine chased off more mosquitoes than chemical solutions that mirrored those of intact leaves, the study found.
The team also presented cats with two dishes — one with intact silver vine and one with damaged leaves. Without fail, the cats would go to the damaged leaf container and lick and play with the dish and roll against it.